|
The Forsyth-Edwards Notation (FEN for
short), is the standard notation or method for describing Chess positions or
a particular board position of a Chess game. It was created in 1883 by newspaper
journalist David Forsyth from Scotland and slightly extended later by an
American computer scientist Steven J. Edwards for use in computer Chess
software. The main purpose of FEN notation files is to provide all the
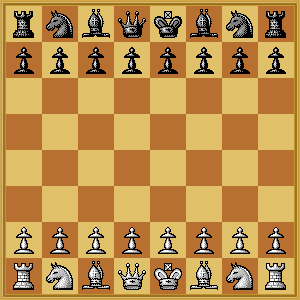
information required to restart a game from a desired Chess position. Typical FEN string showing the Chessboard
initial position:
FEN strings contain separators between
fields using blank spaces:
Field #1: Chess
pieces setup: This field number 1 is comprised of 8
strings or sections of letters and numbers separated by slashes ( / ):
Each string or section represents a rank
or a row of 8 squares of the Chess board running from left to right and starting
from the uppermost section of the board (black pieces). Every rank is filled
up with letters taken from the standard English names: “P”= Pawn, “N”=
Knight, “B”= Bishop, “R”= Rook, “Q”= Queen, “K”= King, and numbers from 1 to
8. White pieces are identified by uppercase letters (PNBRQK) and black pieces
by lowercase letters (pnbrqk). Adjacent or contiguous empty squares are
identified with a single digit number (1 to 8), e.g.: a whole empty row of 8
squares should be represented by an “/8/”, not as “/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/1/” and
this also applies to any other lower amount of contiguous empty squares in a
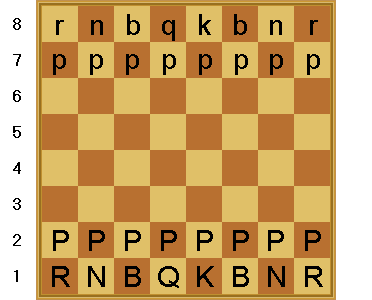
row. The following image is an alternate way
of visualizing the board with the above FEN file:
|
References
http://www.chess-poster.com/english/learn_chess/notation/notation.htm